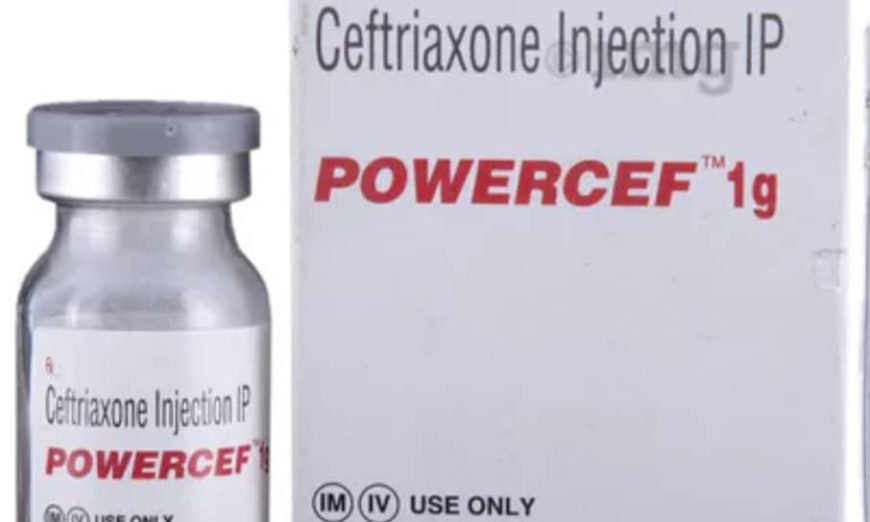
AN investigation by SAUTI KUBWA targeting the application of Powercef to patients in health centers of three districts of Dar es Salaam in Tanzania has revealed that the antibiotic is being overused.
The 21-day journalistic investigation in six health centers, two polyclinic and one dispensary has proven that almost all patients visiting those health facilities in Kinondoni, Ilala and Ubungo, were prescribed with Powercef, an intravenous shot whose generic name is Ceftriaxone.
Our reporters managed to find out that the main reason for the overuse of Powercef was all pegged on patients’ claims of a speedy relief after applying it.
Powercef is regarded a “hand-of-God drug” by some medical personnel we interviewed – as it is fast and effective in treating a wide range of bacterial diseases like meningitis, pneumonia, Urinary Tract Infections (UTI), some sexual transmitted diseases (STDs) and other infections in human body.
In the centres that our reporters visited, one shot of Powercef is sold at Tanzania Shillings between 6,000 and 7,000.
It appears that Powercef is among the fast moving antibiotic in famous pharmacies.
A pharmacist at Plus Pharmacy in Buguruni says that Powercef is a quick-moving item now. “I think it is among the widely use drug for now, it is a huge selling item which means it is a trusted treatment,” she says.
Penina Mwangoka, a pharmacist who declined selling Powercef to our reporter as he had no prescription from a doctor, admits that a lot of people are frequenting her pharmacy, asking for the wonder drug without having medical recommendation.
A medical doctor, Kassim Mwaluko, from Nyota Njema Dispensary in Mwenge, says that Powercef, which is not recommended for use in newborns and premature infants due to its increased risk of side effects, should be prescribed only by trained medical personnel after laboratory investigations.
“Powercef, as the name shows, is so powerful and effective in treating some infections, but it has got some side effects if wrongly applied by a patient; so it should not be taken as a first line treatment on every sickness like what many of my colleagues are doing,” he cautions.
Dr. Mwaluko pleads to his fellow medical practitioners to prescribe Powercef only after laboratory investigations.

Accordig to him, some of the side effects of Powercef include easy bleeding, unusual tiredness, symptoms of gallbladder disease – such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, signs of kidney problems, painful and sometimes frequent urination, back/side pain and uncontrollable movements.
A medical professor from the Muhimbili National Referral Hospital who prefers anonymity, says the overuse of Powercef as a first line of treatment in every kind of bacterial infection will render it ineffective in the long run.
He says it is ideal for all doctors to rely on the medial investigations results from laboratories before prescribing powerful antibiotics, including Powercef.
The professor says the shortage of laboratory facilities, and the lack of enough healthcare professionals would eventually lead to major medical hiccups, particularly drug resistance.
Country’s Chief Medical Officer (CMO) Dr. Aifello Sichalwe admits the antibiotic is in higher demand than other “common” antibiotics, like Tetracycline and others.
He says the high demand may be a result of the drug’s effectiveness as well as its availability in the country. But he also advises doctors not to recommend it as a first line medication in every case.
“I am so optimistic that doctors know when and how to prescribe a patient with Powercef but they must be vigilant not to abuse it so that it doesn’t become resistant because of being overused,” he warns.
Just recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced a rapid emergence of antimicrobial resistance in some STDs, including gonorrhea to a range of antibiotics with no new therapeutic agents being produced.
Gonorrhea, represents 88 million of the estimated 448 million new cases of curable STDs – that also includes syphilis and chlamydia – which occur globally every year.
WHO said gonorrhea may thus become virtually untreatable. Action is needed to contain antimicrobial resistance to gonorrhea as well as to put in place a mitigation strategy to prevent eventuality.